What is RFID?
RFID = Radio Frequency IDentification.
An ADC (automated Data Collection) technology that:
- Uses radio-frequency waves to transfer data between a reader and a movable item to identify, categorize, track..
- Is fast and does not require physical sight or contact between reader/scanner and the tagged item.
- Performs the operation using low cost components.
- Attempts to provide unique identification and back-end integration that allows for wide range of applications.
Other ADC technologies: Bar codes, OCR.

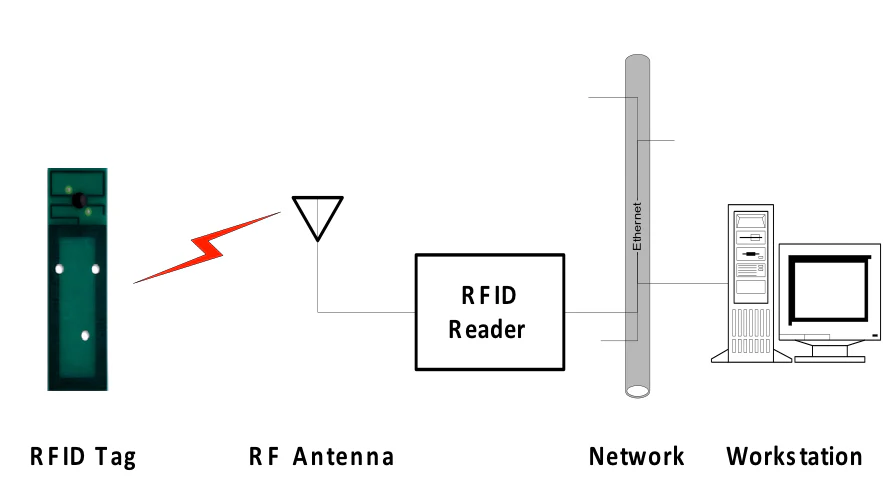
RFID systems: Logical view

RFID tags: Smart labels

RFID Examples:

RFID Tags:
Tags can be attached to almost anything:
- Items, cases or pallets of products, high value goods
- vehicles, assets, livestock or personnel
Passive Tags
- Do not require power – Draws from interrogator Field
- Lower storage capacities (few bits to 1 KB)
- Shorter read ranges (4 inches to 15 feet)
- Usually Write-Once-Read-Many/Read-Only tags
- Cost around 25 cents to few dollars
Active Tags
- Battery Powered
- Higher storage capacities (512 KB)
- Longer read range (300 feet)
- Typically can be re-written by RF interrogators
- Cost around 50 to 250 dollars

Read-only tags
- Tag ID is assigned at the factory during manufacturing
- Can never be changed
- No additional data can be assigned to the tag
Write once, read many (WORM) tags
- Data written once, e.g., during packing or manufacturing
- Tag is locked once data is written
- Similar to a compact disc or DVD
Read/Write
- Tag data can be changed over time
- Part or all of the data section can be locked
RFID readers
- Reader functions:
- Remotely power tags
- Establish a bidirectional data link
- Inventory tags, filter results
- Communicate with networked server(s)
- Can read 100-300 tags per second
Readers (interrogators) can be at a fixed point such as:
- Entrance/exit
- Point of sale
Readers can also be mobile/hand-held

Reader Anatomy

RFID Application Points

RFID Applications
Manufacturing and Processing
- Inventory and production process monitoring
- Warehouse order fulfillment
Supply Chain Management
- Inventory tracking systems
- logistics management
Retail
- Inventory control and customer insight
- Auto checkout with reverse logistics
Security
- Access control
- Counterfeiting and They control/prevention
Location Tracking
- Traffic movement control and parking management
- Wildlife/Livestock monitoring and tracking
Smart Groceries

- Add an RFID tag to all items in a grocery store
- As the cart leaves the, the cart passes through an RFID transceiver.
- The cart the gets totaled up in a matter of seconds.
Smart Cabinet
- Tagged item is removed from or placed in the “Smart Cabinet”
- The Smart Cabinet periodically interrogates to assess inventory
- Server/Database is updated to reflect item’s disposition
- Designated individual are notified regarding items that need attention (cabinet and shelf location, action required)

Smart Fridge
- Recognizes whats been put in the fridge
- Recognizes when things are removed
- Creates automatic shopping lists
- Notifies you when things are past their expiration date
- Shows you the recipes that most closely match what is available
Smart Groceries Enhanced
Track Products through their entire lifetime.
More Smart Applications:
“Smart” Appliances:
- Closets that advice on style depending on clothes available
- Ovens that know recipes to cook pre-packaged food
“Smart” products:
- Clothing, appliances, CD’s etc. Tagged for store return.
“Smart” Paper:
- Airline tickets that indicate your location in the airport
“Smart” currency:
- Anti-counterfeiting and tracking.
RFID Advantages over bar-codes
- No line of sight required for reading
- Multiple items can be read with a single scan
- Each tag can carry a lot of data (read/write)
- Individual items identified and not just the category
- Passive tags have a virtually unlimited lifetime
- Active tags can be read from great distances
- Can be combined with bar code technology